What Is Bitcoin? – An easy to digest User Guide to Bitcoin
Bitcoin is two things. It is both a cryptocurrency, and the underlying technology – a worldwide payment system.
What Is Bitcoin? – Bitcoins as Digital Assets
Common reference and associated terms: Bitcoin, bitcoin, digital currency, cryptocurrency, virtual currency, digital cash, and electronic currency.
Bitcoins are commonly referred to as ‘digital assets’, i.e. they have no physical form.
Bitcoins are not printed or minted like traditional fiat currencies such as British Pound Sterling, Euros or US Dollars. Instead, they are created digitally, through computer processing methods, and stored digitally.
Traditional fiat currencies might physically be stored in your wallet, or in a bank vault. Whereas digital assets such as Bitcoin are stored on computer hard drives, or on servers hosted around the world or in the Cloud.

Bitcoin is widely regarded as being the world’s first de-centralised digital currency. That is, it operates without the need for or oversight from any central bank or governing body. The removal of an intermediary, or “middle man” in this way, is a big benefit and attractive aspect of Bitcoin for many users.
The Bitcoin ecosystem is distributed across a network of users and system administrators. All of who might be located in any country around the World.
Furthermore, the underlying technology (Blockchain) and code base upon which Bitcoin is built, is open source. Meaning any developer or group of developers can view, interrogate, and critique it, and then propose their own improvements or alternative implementations.
What Is Bitcoin? – Who created Bitcoin?
Bitcoin was created by a developer (or group of developers) going by the pseudonym of ‘Satoshi Nakamoto’.
Satoshi might well be individual developer, or a guise taken on by a group of developers wanting to protect their anonymity.
No one really knows.
As a lasting acknowledgement of Satoshi Nakamoto, the smallest denomination (fraction) of a Bitcoin is called a Satoshi.

What we do know is that in 2008 Satoshi Nakamoto published a ‘white paper’ which is widely accepted as the first published proposal for Bitcoin. The proposal outlined a new means of electronic exchange, based upon cryptography and the concept of Blockchain. A system which would offer secure, verifiable transactions across a peer network, without the need for a central authority (bank or middleman payment system).
What Is Bitcoin? – How the Bitcoin network works
The Bitcoin payment system makes use of a distributed network of connect peer ‘nodes’. Each node is effectively a computer or server running the Bitcoin software, and serving the Bitcoin network. Each Bitcoin transaction is confirmed and verified by the network of nodes.

Think of it as “crowd sourcing” for transactions. In this way, each node retains a copy of all Bitcoin transactions to date. Typically this is called a Bitcoin Ledger. The nodes constantly check in and sync their copy of the ledger with the rest of the network. This ensures agreement and maintains a trusted register of transactions.
The actual verification is achieved using Cryptography and a method called ‘Proof of Work’ which is computationally expensive and time consuming. As transactions are confirmed, they are grouped into ‘Blocks’.
As these blocks build and proliferate over time, a chain of blocks is created. Thus, the ‘Blockchain’ is created. The Bitcoin Ledger effectively contains a record of the current Blockchain.
What Is Bitcoin? – Bitcoin Mining
Bitcoin Mining is essentially the process of confirming Bitcoin transactions and maintaining the Blockchain, in exchange for Bitcoin rewards. It’s a little more involved than that though, so let’s look at what this process is and why it has arisen.
What Is Bitcoin? – Cost and Reward associated with Bitcoin Mining
The expense incurred in setting up and hosting dedicated computer hardware or servers to run the Bitcoin software provides a barrier to entry.
High performance processing units cost money, as does the electricity to keep them running.
This barrier to entry isn’t necessarily a bad thing. It deters just anyone from having a go and joining the network. This goes some way to ensuring that the peer network contains predominantly only nodes dedicated to serving the Bitcoin payment system. Ensuring reliability and access to processing power.
It takes significant computing effort, time and electricity to complete the ‘Proof of Work’ required to confirm Bitcoin transactions and add a ‘Block’ to the Blockchain ledger.
This whole process is commonly referred to as ‘Bitcoin Mining’, which itself is an analogy to the process of traditional Gold Mining.
A lot of physical effort and time is expended, but the outcome (obtaining Gold) outweighs the initial investment and rewards the speculator handsomely.

In return for their efforts, operators of these nodes are rewarded with newly minted increments of Bitcoin. With the current market value of Bitcoin, this can make Bitcoin Mining economically viable and indeed very lucrative.
What Is Bitcoin? – The conditions surround Bitcoin Mining change over time
In the early days of Bitcoin, the computational effort required to ‘prove’ a block on the Blockchain was low. The difficulty of the computation was low enough to entice even amateur enthusiasts. They would hook-up their desktop computer or laptop to the Bitcoin network, run the Bitcoin software and be in the fight for Bitcoin mining rewards.
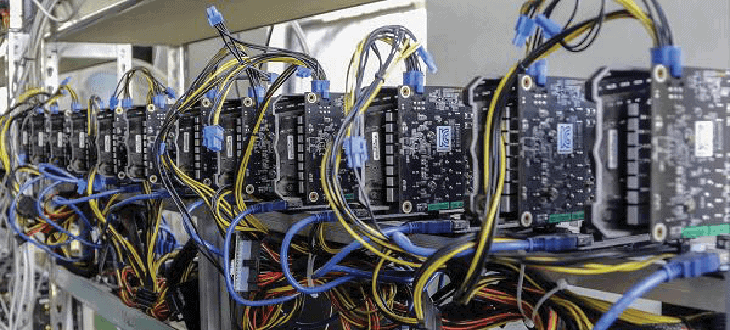
However in recent years, with the growing popularity and increased use of the Bitcoin network, this has become near impossible. The mining difficulty has increased significantly – ramping up the computing power and electricity consumption required to successfully mine or prove a block.
As such, Bitcoin Mining has now become almost exclusively the realm of well funded, and technically advanced mining outfits. These mining outfits typically group their resources together to form ‘Mining Pools’ and build dedicated ‘Mining Farms’ just for the purpose of Bitcoin Mining.
Mining farms are server farms – consisting of racks of dedicated processing units, all running 24-7, 365 days a year. All of these Mining farms are maintaining the Bitcoin transaction network and ‘mining’ to prove the next block on the Blockchain and win new Bitcoin.
What Is Bitcoin? – How else can people get their first Bitcoins?
New Bitcoin users can typically acquire Bitcoin through any of the following ways:
- By signing up to and then purchasing some Bitcoin from a reputable Bitcoin exchange (good examples being Binance, Coinbase, or CEX.io)
- By winning free Bitcoins from Free Bitcoin Faucets, through competitions or similar promotions
- By setting up a Bitcoin wallet, which then receives an amount of Bitcoin from a friend or relative who already has some Bitcoin
- By earning it in exchange for running the Bitcoin software on their computer(s) or servers – this is called Bitcoin Mining
